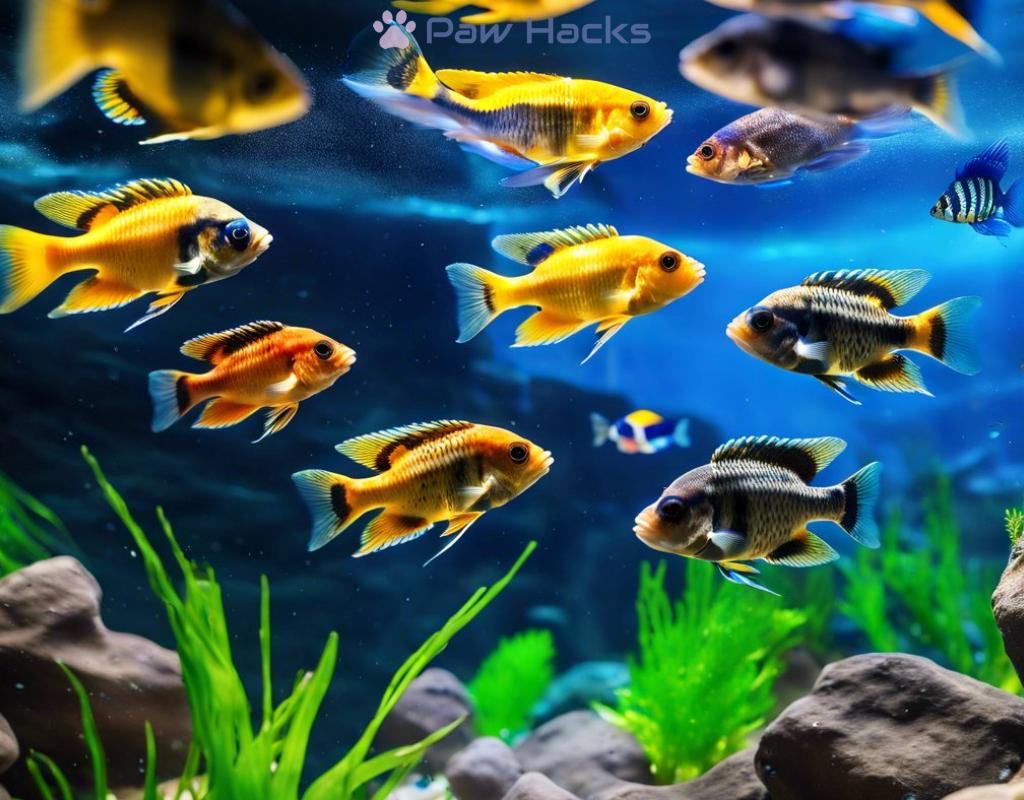
Feeding Habits of African Cichlids
Understanding the Diverse Diets of African Cichlids

African cichlids are known for their stunning colors and diverse sizes, but their feeding habits are equally fascinating. These fish originate from the various lakes of Africa, particularly Lake Malawi, Lake Tanganyika, and Lake Victoria. Each environment presents unique challenges and resources, leading to a variety of feeding strategies that are adapted to their specific habitats. Understanding these strategies provides insight into their behavior and ecology, making them all the more intriguing to aquarists and nature enthusiasts alike.
In the wild, cichlids exhibit different feeding patterns based on their species. Some are herbivores, others are carnivores, and many are omnivores. This diversity not only influences their diet but also impacts their interactions within their ecosystems.
To appreciate the complexity of African cichlids’ diets, it is essential to categorize them into specific dietary types. Each type of diet corresponds to unique physical adaptations and behaviors. Here’s a closer look at the primary diet categories:
- Herbivores: These cichlids primarily feed on algae and plant materials. They have specialized teeth for scraping surfaces to obtain their food.
- Carnivores: These species prey on smaller fish, invertebrates, and other animal matter. Their teeth are sharp and designed for grasping and tearing flesh.
- Omnivores: A versatile group, omnivores consume both plant and animal matter. They exhibit flexible feeding behaviors, allowing them to thrive in various environments.
The feeding habits of African cichlids play a crucial role in their ecosystems. Their dietary choices influence the health and balance of their aquatic environments. For instance, herbivorous cichlids help control algae growth, while carnivorous species regulate fish populations. This dynamic interplay showcases the importance of each species within its habitat.
Furthermore, cichlids often exhibit territorial behaviors around feeding areas, which can lead to competition not just among their own species, but also with other fish. This competitive nature emphasizes the adaptability and resilience of these remarkable fish in their quest for survival.
The Role of Habitat in Cichlid Feeding Behaviors
In the intricate world of African cichlids, the habitat plays a pivotal role in shaping their feeding behaviors. Each lake, with its distinct characteristics, influences not only the availability of food but also the adaptations that cichlids develop over time. For aquarists and fish enthusiasts, understanding these dynamics is crucial for creating suitable environments that mimic their natural habitats.
The diverse habitats of African lakes can be broken down into several key categories, each fostering different feeding strategies among cichlid populations. Below is a comparative overview of these environments and their impact on feeding behaviors:
| Habitat Type | Characteristics | Feeding Adaptations |
|---|---|---|
| Rocky Shores | Provide shelter and abundant algae growth | Specialized teeth for scraping and grazing |
| Open Water | Characterized by less structure and more open space | Sharp teeth and fast swimming for catching prey |
| Submerged Vegetation | Rich in plant life and invertebrates | Flexible feeding habits, allowing for omnivorous diets |
The dynamic interactions among cichlids in their habitats also reveal much about their feeding behaviors. Territorial disputes often arise around food sources, leading to fascinating displays of aggression and hierarchy. However, some species have developed cooperative strategies to maximize feeding efficiency. Understanding these interactions can deepen our appreciation for the complexity of cichlid communities and their remarkable adaptations.
How to Choose the Right Food for Your Cichlids
When it comes to keeping African cichlids, selecting the right food is crucial for their health and vibrant coloration. These fish have specific dietary needs that vary according to their natural feeding habits and habitat. Understanding these needs not only enhances their well-being but also ensures that they thrive in your aquarium environment.
Each cichlid species comes with its own dietary preferences, which are often linked to their natural feeding habits. For example, herbivorous cichlids benefit from foods rich in plant material, such as spirulina flakes or algae wafers, which mimic the algae they consume in the wild. On the other hand, carnivorous species thrive on high-protein diets that include freeze-dried or frozen foods, such as bloodworms and brine shrimp. Understanding these preferences is essential for maintaining their health, as improper feeding can lead to malnutrition or even disease.
When selecting cichlid food, always prioritize nutritional value over sheer quantity. High-quality foods are often richer in essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins that promote growth and coloration. Look for products specifically formulated for African cichlids, as these often provide a balanced diet tailored to their unique needs. Furthermore, consider incorporating a variety of foods into their diet to ensure a well-rounded nutritional intake, mimicking the diversity found in their natural habitats. This variety not only keeps your fish healthy but also stimulates their natural foraging instincts.
In conclusion, the right food can make all the difference in the health and vitality of your African cichlids. By aligning their diet with their natural feeding habits and ensuring high-quality nutrition, you can create a thriving aquarium environment that showcases the beauty and diversity of these remarkable fish.
The Impact of Feeding Frequency on Cichlid Health
Feeding frequency plays a crucial role in the overall health and well-being of African cichlids. Just as their natural feeding habits vary widely among species, so too does their response to the frequency of feeding. This aspect is often overlooked by aquarists, yet it can significantly influence the vitality of these vibrant fish. Establishing a proper feeding schedule not only meets their nutritional needs but also mimics the rhythms found in their natural environments.
Regular feeding schedules are essential for maintaining the health of African cichlids. Unlike some fish species that thrive on sporadic feeding, cichlids generally benefit from frequent, small meals throughout the day. This approach mirrors their natural behavior, where they graze on algae or hunt for food consistently. By providing meals at regular intervals, aquarists can help prevent issues such as overeating, which can lead to health complications like obesity or swim bladder disease. Regular feeding not only promotes better digestion but also contributes to more vibrant coloration and overall vitality.
While frequency is important, it is equally vital to balance the quantity and quality of the food provided. Cichlids require a diet rich in nutrients tailored to their specific dietary needs. Offering a variety of high-quality foods can ensure that they receive essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins necessary for growth and health. Overfeeding, even when done frequently, can lead to poor water quality and health risks. Therefore, monitoring portion sizes and adjusting feeding frequency based on the fish’s response is advisable. A good rule of thumb is to feed them only as much as they can consume within a few minutes, ensuring that uneaten food does not decay in the tank.
Ultimately, the impact of feeding frequency on cichlid health cannot be understated. By understanding their dietary behaviors and preferences, aquarists can create an environment that closely resembles their natural habitats. This not only enhances the health of the fish but also enriches the aquarium experience for enthusiasts, allowing them to witness the stunning displays of activity and color that African cichlids are known for.
Exploring the Unique Feeding Strategies of Different Cichlid Species
In the vibrant world of African cichlids, each species exhibits distinct feeding strategies that reflect their adaptations to specific environments and dietary needs. This fascinating diversity not only enhances their survival but also showcases their unique behaviors. By delving into the various feeding strategies of these remarkable fish, aquarists and enthusiasts can gain a deeper understanding of their care requirements and ecological significance.
Each cichlid species has evolved specialized feeding techniques that cater to their dietary preferences. For instance, herbivorous cichlids have developed a unique set of teeth designed for grazing on algae and plant matter. These fish often have flat, grinding teeth that allow them to scrape algae off rocks and surfaces efficiently. In contrast, carnivorous cichlids possess sharp, pointed teeth that are adept at grasping and tearing their prey, which typically includes smaller fish and invertebrates. This specialization not only aids in their feeding efficiency but also minimizes competition among species, as each occupies a distinct niche within their habitat.
The social structure among cichlid species significantly influences their feeding strategies. Many cichlids display territorial behaviors that establish dominance over feeding grounds. This territoriality can lead to aggressive displays and competition for food resources, particularly in species that thrive in similar environments. However, some species have developed cooperative feeding strategies, allowing them to forage together in groups. This collaboration can enhance their foraging success, particularly in environments where food is scarce. Understanding these social dynamics can help aquarists create a more harmonious environment, reducing stress and promoting healthier feeding habits.
In conclusion, the feeding strategies of African cichlids are as diverse and intriguing as the fish themselves. By appreciating these unique adaptations and behaviors, aquarists can better cater to the needs of their cichlids, ensuring a thriving aquarium that mirrors the complexities of their natural habitats.
Share this content: